Communication Guidebook - 10-12 (High School) Sun West
Communication High School 10-12
Purpose
Why is this important?
Communication is one of the key components of 21st-century learning, yet it has not attracted the same level of research or attention as creativity, collaboration, or critical thinking. Communication competence involves mediated and digital communication, interpersonal, written and oral communication. As our society evolves, we cannot assume that our students will gain communication competence on their own.
Practical communication skills are needed for all students
- Speech-language development is a key aspect of preschool and early learning
- Social and emotional learning studies address positive classroom communication interventions
- Business-related communication assessments (like the elevator pitch assessment) are also applicable to education contexts
- Digital and media literacy provide unique approaches to analyzing communication skills
- Additional research and interventions are needed to support 21st-century communication skills
Communication. P21 Partnership for 21st Century Learning. http://www.p21.org/our-work/4cs-research-series/communication. Web. May 7, 2018
Explicit Teaching
To be able to learn and grow in 21st Century Competency understanding, it is important to teach each skill and let students experience what each skill looks like as well as how you can grow in each area. Caution: by simply saying the word "communication or collaboration...etc" students may not get a full understanding of each skill. Explicitly teaching and utilizing skills in different ways is what will ultimately promote deep understanding and growth in 21st Century Comptencies.
Timeline Suggestions for Explicit Teaching
The document below provides a year plan to teach each of the 21st century skills. It is beneficial to have an explicit teaching plan to ensure each skill is taught; however skills should also be reinforced as much as possible throughout class time.
Lesson Plans
Share Learning
The following activities and resources are for teaching students how to share their learning experiences.
It is important to share your knowledge for a variety of reasons:
1. It helps you grow
· Having a fixed set of skills makes you proficient in a specific area, but sharing skills and knowledge with other people allows you to continually grow and develop in other areas.
2. It helps you stay motivated
· Sharing knowledge with peers pushes you to become better while driving you to contribute with your own thoughts and insights.
3. Allows you to become the best you can be
· Knowledge sharing can help with getting feedback to be able to make changes and can help you with projects by getting different information from different people with different competencies.
4. Recognition
· Sharing your knowledge will give others the opportunity to see your talents and strengths. Being recognized for your strengths is a great motivator to continue to push yourself.
5. Closing the Skill Gap
· Recognizing your strengths and weaknesses, and talking about them will allow you to better set goals to be able to achieve and strengthen new skills.
Activity: Closing Circle
End of day discussion centred around “who, what, where, when, why?” For example, Who gave you a different insight into something today? What is something new you learned from that person? When might you try and use this new skill/method/etc…? Why did you find this interesting? Why do you think you might try something different than what you were currently doing? Etc…
This activity could be done discussion format or journaling format.
Cooperate
Communication Skills Activities
A website full of different communication skill activities. Just a few to mention are:
- Communication origami (shows how the same instructions can be interpreted differently, and how important clear communication is)
- Guess the emotion (focused on students becoming more aware of their feelings or emotions)
- Power of Body Language (an activity that shows how powerful the effect of body language is in communicating with others)
- Room 101 (practice persuasive skills in focusing on choosing positive language, being passionate and enthusiastic, etc.)
https://www.trainingcoursematerial.com/free-games-activities/communication-skills-activities
Bridging the Communication Gap Between Parents & Children (may be applicable to Teacher/Student)
https://childdevelopmentinfo.com/parenting/parent-child-communication/#.WvMUw4gvyUk
Communication Skills Lesson
http://awrcsasa.ca/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/Example-HRY-Session.pdf
Communication Activities Lesson – from the Fremont Unified School District
Looks like an awesome resource with a ton of activities in it! Some of the activities include:
- Self-Appraisal Communications Survey
- Body Language
- Nonverbal Cues
- Practice Listening Skills
- Practising Communications Skills
Build Team Strengths
The Art of Persuasion – Warmups and Drills to Develop Your Skills (Dr. Rick Kirschner)
“It’s one thing to have a lofty idea. It’s another thing entirely to bring that idea to fruition. This is where the rubber meets the road, where action speaks louder than words, and where it’s not what you know but what you do with what you know that counts. This is how to make your communication count.”
http://learntopersuade.com/PlaybookwCvr.pdf
Scholastic Lesson Plan – The Game of Persuasion
Teach students to “argue” productively! In this lesson, they learn how to develop and present persuasive arguments to the class.
https://www.scholastic.com/teachers/lesson-plans/teaching-content/game-persuasion/
Evaluate the Team
Reflective Thinking
http://www.hawaii.edu/intlrel/pols382/Reflective%20Thinking%20-%20UH/reflection.html
15 ways to spark student reflection in your classroom
https://www.nureva.com/blog/15-ways-to-spark-student-reflection-in-your-classroom
Reflection Activities
This is an entire PDF full of reflection activities to enhance students’ learning experience. It was compiled by Professor Diane Sloan from Miami Dade College. They are activities geared towards college-aged students, but I think could be easily adapted for the high school classroom.
http://www.usf.edu/engagement/documents/s-l-reflection-activities.pdf
4-H reflection Activities
Find solutions
Encouraging your Students to Give Feedback
- Being able to model the acceptance of feedback (good or bad) is a good way to encourage acceptance of feedback in your students.
Article by Marilla D. Svinicki – “Giving feedback is a skills that can be learned. What are the conditions that foster that learning and the later use of that skill for feedback to instructors?”
https://www.jcu.edu.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0016/105091/jcu_121460.pdf
Receiving and Giving Effective Feedback
University of Waterloo Article
Receiving Feedback
http://www.workshopexercises.com/Feedback_Receiving.htm
18 Active Feedback Exercises
http://reviewing.co.uk/archives/art/3_9.htm#2
Giving and Receiving Feedback
Carleton University – “How To’s”
https://serc.carleton.edu/introgeo/peerreview/feedback.html
Integration of Skills
Intentional integration of 21st Century Competency language in all day-to-day activities supports the development of routine reflection, skill use, and growth in support of curricular knowledge acquisition.
Why?
If we do not intentionally integrate 21st Century Competency connections into our learning environments, it is easy to forget about them. As the language becomes routine, growth in skills can and should be explored regularly. Ultimately the 21st Century Competencies are the skills needed to be successful in all day-to-day activities as well as future career opportunities. By being intentional in integrating the language and skill use in all aspects of learning, understanding of the skills can be applied and reflected upon to look for areas of potential growth and application.
How?
Once skills have been explicitly taught, integration of 21st Century Competencies can be achieved by connecting skills to all curricular areas, participating in pre-and post reflections (allowing students to predict which skills will be needed and subsequently which skills need to be worked on) and the use of 21st Century Competency rubrics to track growth.
Example: by using learner profile data, students can reflect on which skills they need to employ for a particular activity and based on this information, choose group members that have strengths or challenges in those skill areas.
Examples
When integrating 21 Century Competency language in all areas of learning consider the following curricular connected resources.
As you use similar resources in your own learning environment, how can you relate them back to growth and understanding of the 21 Century Competencies?
In ELA
This will likely be your focus area with communication. Be sure to include regular lessons on the following topics, and providing ample opportunity to practice, share and reflect.
- Sharing work in a variety of ways - including guiding reading groups, short oral presentations, participating in class and small group discussions, sharing stories and research, trying different forms of multi-media and written presentations, conferences, interviews, etc.
- Explicitly teaching the art of persuasion, including argumentative or persuasive writing, debate, clarifying fact vs. opinion when forming arguments, and respecting the opinions of others & how to disagree in a positive manner and respectfully, and the difference between manipulation & persuasion.
- Providing opportunities for students to practice being clear and concise by providing regular feedback, doing check-ins with peers or teacher, and checking for understanding and clarity. Explicitly teaching the skill of summarizing and paraphrasing will be important to develop clarity.
- Provide opportunities to invite feedback at all stages of writing or working from self, peers and the teacher or parents. Discuss how to accept and give positive criticism (this can be difficult even for adults, so honour that this may not be easy for your students!). Practice ways to provide feedback by still recognizing the positive features of the work (For example, 2 stars and 1 wish, or starting with a positive before adding a negative.). Be sure to teach students how to use feedback to improve their work. Revising is key here!
Creating Psychological Profiles of Characters in To Kill a Mockingbird
Exploring Language and Identity: Amy Tan's "Mother Tongue" and Beyond
RAFTS: Roles, Audience, Format, Topic & Strong Verb
Joining the Conversation about Young Adult Literature
Writing Strategies for the Classroom
Writing Traits/Qualities/Strategies
Draft Letters: Improving Student Writing through Critical Thinking
Persuading an Audience: Writing Effective Letters to the Editor
Nanotechnology Grant Proposal Writing
In Math
Communication is important in all areas of school and life, and should also be discussed, modelled and used in Math. Be sure to include the following opportunities for your students:
- Provide them with opportunities to share their work in math in a variety of ways as well including pairs, small groups and class. Consider building capacity in student and having them lead a re-teaching or teaching session to allow them to share their work. Students can make videos to explain math concepts clearly for peers using PowToon or other video editors.
- Allow students to share their answers, and explain how they arrived at it to work on persuasion. Maybe someone has a different way to approach a problem - variety is good!
- Clarity and being clear will likely be your focus in Math. Teach students how to attack word problems and find what is actually being asked. Used strategies like circling or underlining key words, re-reading, covering it and explaining the question to a friend, etc. You'll also want to address making your answer clear in math. Teach the kids how to make their answer easy to find using a variety of methods such as circling or boxing the answer, using, therefore, symbols or statements, etc.
- Students can also provide one another with feedback on how the approached a solution to a problem, and if they were able to follow the other's thinking, and if things are clear. Allow students the opportunity to reflect, as well as get feedback from peers and the teacher in math.
Teachable moments
Whenever a question, situation, comment or activity that involves a connection to a 21 Century Competency arises, take a moment to talk to students about it. Discussing skills, how they integrate into everything you do in life makes the reflection on the importance of skills a habit. This habit will instill a growth mindset around developing skills to their fullest potential. Teachable moments can be as short as 20 seconds. Make it your habit and it will become theirs!
Tracking Growth
When considering 21st Century Competency application, it is essential for both the teacher and the student to track growth. There is clear potential for growth in skill use throughout our lives. To ensure growth and understanding of application is taking place, we can easily track progression using rubrics, checklists, and self-assessments.
Formative Assessment
Formative assessments of 21st Century Competencies include anecdotal documentation, self-assessments and rubric check-ins. These formative assessments provide snapshots of growth throughout the learning process and allow goal setting to take place.
Assessing Growth
Summative Assessment
Exemplar Rubrics
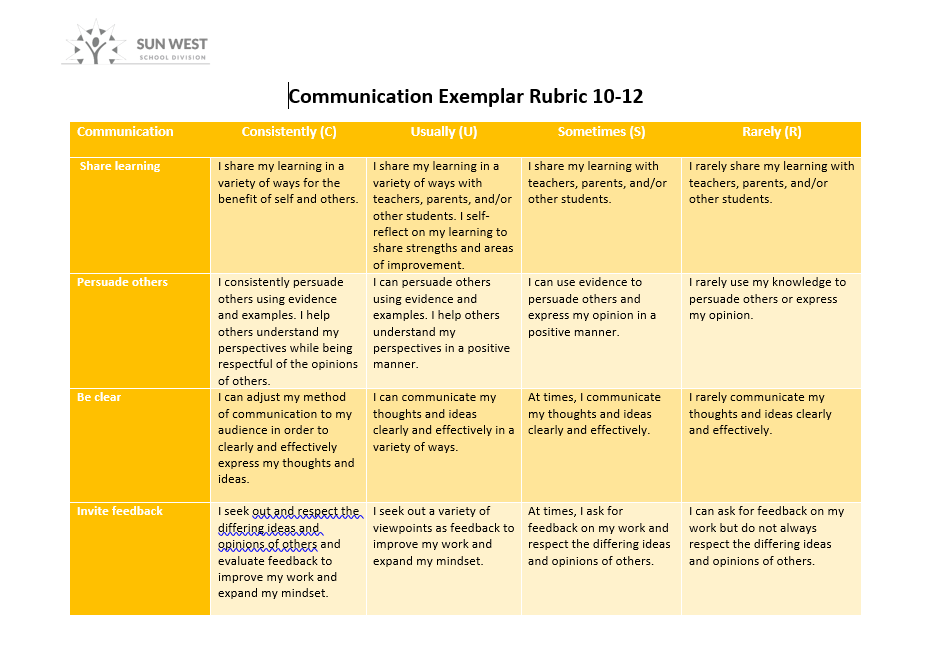
Communication 10-12
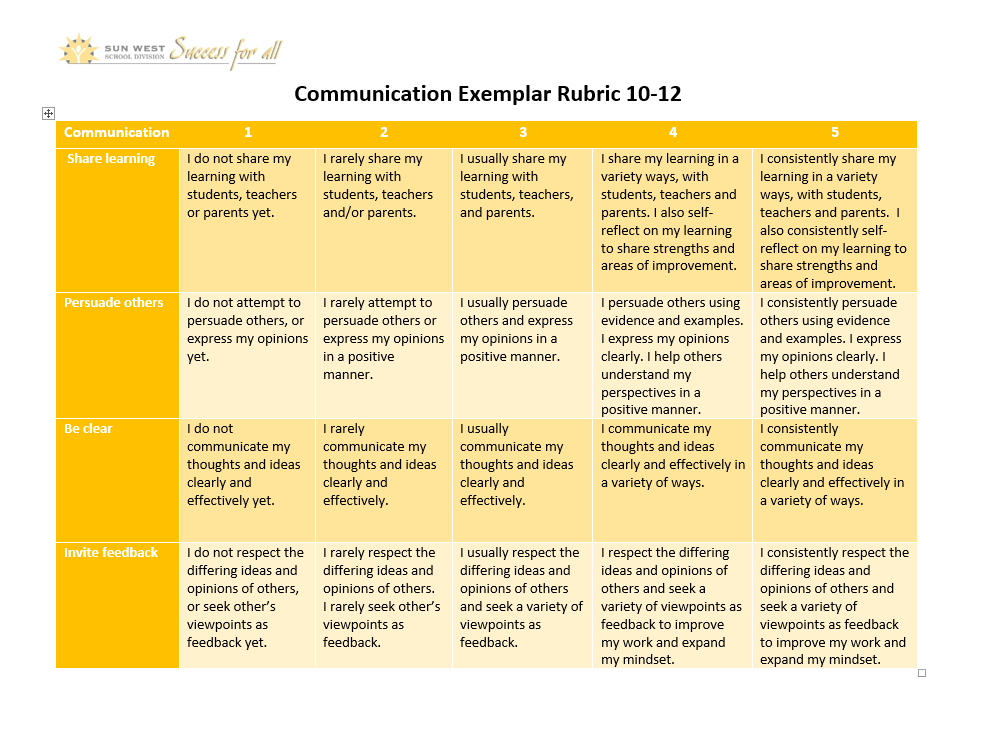
Communication 10-12 Rubric
Co-creating Rubrics
Exemplar rubrics have been developed for K-5, 6-9 and 10-12. To connect fully with students in their understanding of skill application and growth, a recommendation would be to re-write the rubric with the students to include their understanding of the skill, goals for integration in learning and commitment to the skill development
Resources
Print based
Sun West Original Print Based Communication 10-12 Guidebook
Digital Citizenship Education in Saskatchewan Schools
The Sun West Technology and Research Continuums both contain skill sets relevant to communication. Please use these as reference points when explicitly teaching communication skills.
Videos
A Better Way to Talk about Love
How Miscommunication Happens (and how to avoid it)
In on a Secret? Dramatic Irony
Situational Irony: The Opposite of What You Think
Future Ready: Examples of Personalized Learning
Interactive
Educational Articles
Web Sites
Alternatives to PowerPoint Presentations
Detail Drawings: Communicating with Engineers
