
"Find out what it's like on other planets. Learn how far away the stars are. Try a fun, space-themed project."
- Subject:
- Science
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Primary Source
- Date Added:
- 05/25/2020

"Find out what it's like on other planets. Learn how far away the stars are. Try a fun, space-themed project."

When we look at the night sky, we see stars and the nearby planets of our own solar system. Many of those stars are actually distant galaxies and glowing clouds of dust and gases called nebulae. The universe is an immense space with distances measured in light years. The more we learn about the universe beyond our solar system, the more we realize we do not know. Students are introduced to the basic known facts about the universe, and how engineers help us explore the many mysteries of space.

Students are introduced to our Sun as they explore its composition, what is happening inside it, its relationship to our planet (our energy source), and the ways engineers help us learn about it.

Students learn how the total solar irradiance hitting a photovoltaic (PV) panel can be increased through the use of a concentrating device, such as a reflector or lens. This is the final lesson in the Photovoltaic Efficiency unit and is intended to accompany a fun design project (see the associated Concentrating on the Sun with PVs activity) to wrap up the unit. However, it can be completed independently of the other unit lessons and activities.

Students design, build and test reflectors to measure the effect of solar reflectance on the efficiency of solar PV panels. They use a small PV panel, a multimeter, cardboard and foil to build and test their reflectors in preparation for a class competition. Then they graph and discuss their results with the class. Complete this activity as part of the Photovoltaic Efficiency unit and in conjunction with the Concentrated Solar Power lesson.

Students learn about using renewable energy from the Sun for heating and cooking as they build and compare the performance of four solar cooker designs. They explore the concepts of insulation, reflection, absorption, conduction and convection.
This 8-minute video lesson examines the scale of distance from the solar system to the closest stars. [Cosmology and Astronomy playlist: Lesson 3 of 85]

This 10-minute video lesson looks at the scale of the Earth and the Sun. [Cosmology and Astronomy playlist: Lesson 1 of 85]

Students explore the many different ways that engineers provide natural lighting to interior spaces. They analyze various methods of daylighting by constructing model houses from foam core board and simulating the sun with a desk lamp. Teams design a daylighting system for their model houses based on their observations and calculations of the optimal use of available sunlight to their structure.

In this activity, students will test whether the color of a material affects how much heat it absorbs.

Students will explore the relationships and patterns among the Earth, Sun, and Moon system in our solar system. Students will design, build, and test a model of a lunar rover.

In this activity, students use a paper plate to build a model that shows why lunar eclipses don’t happen during every full moon.
"A web portal with comprehensible information on Einstein's theories of relativity and their most exciting applications from the smallest particles to cosmology."
Use the tabs along the menu at the top to find what you need from beginner to more in-depth info.
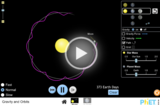
Move the Sun, Earth, Moon and space station to see how it affects their gravitational forces and orbital paths. Visualize the sizes and distances between different heavenly bodies, and turn off gravity to see what would happen without it!

Students explore heat transfer and energy efficiency using the context of energy efficient houses. They gain a solid understanding of the three types of heat transfer: radiation, convection and conduction, which are explained in detail and related to the real world. They learn about the many ways solar energy is used as a renewable energy source to reduce the emission of greenhouse gasses and operating costs. Students also explore ways in which a device can capitalize on the methods of heat transfer to produce a beneficial result. They are given the tools to calculate the heat transferred between a system and its surroundings.

Students examine how the power output of a photovoltaic (PV) solar panel is affected by temperature changes. Using a 100-watt lamp and a small PV panel connected to a digital multimeter, teams vary the temperature of the panel and record the resulting voltage output. They plot the panel's power output and calculate the panel's temperature coefficient.

In this activity, students learn how to prevent exposure to the Sun's harmful ultraviolet rays. Students will systematically test various sunscreens to determine the relationship between spf (sun protection factor) value and sun exposure. At the end of the activity, students are asked to consider how this investigation could be used to help them design a new sunscreen.
One interesting thing about the energy we get from the sun is that it's not absorbed the same way by different materials. In this episode of Crash Course Kids, Sabrina chats about how the properties of land and water differ enough for absorption and reflection.

Students learn how the sun can be used for energy. They learn about passive solar heating, lighting and cooking, and active solar engineering technologies (such as photovoltaic arrays and concentrating mirrors) that generate electricity. Students investigate the thermal energy storage capacities of test materials. They learn about radiation and convection as they build a model solar water heater and determine how much it can heat water in a given amount of time. In another activity, students build and compare the performance of four solar cooker designs. In an associated literacy activity, students investigate how people live "off the grid" using solar power.

Students learn how to find the maximum power point (MPP) of a photovoltaic (PV) panel in order to optimize its efficiency at creating solar power. They also learn about real-world applications and technologies that use this technique, as well as Ohm's law and the power equation, which govern a PV panel's ability to produce power.